Office Management: Essentials for Efficient Workplace Operations
Branch : HR




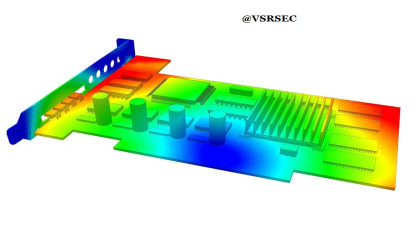
ANSYS is a powerful and widely used engineering simulation software, especially relevant to Mechanical Engineering. It enables engineers to simulate and analyze a wide range of mechanical problems using various physics-based modules.
Here's an overview of how ANSYS is used in Mechanical Engineering:
ANSYS Mechanical is a tool for solving structural problems, including:
ANSYS Mechanical is a tool for solving structural problems, including:
Static structural analysis – stress, strain, and deformation under loads.
Dynamic analysis – vibration, harmonic response, modal analysis.
Thermal analysis – steady-state and transient heat transfer.
Fatigue analysis – prediction of failure due to cyclic loading.
Simulates heat distribution in solids and fluids.
Helps in designing cooling systems, heat exchangers, and thermal insulation.
Supports thermal-stress coupling, useful in cases like brake systems or engine components.
Through ANSYS Fluent or CFX, engineers can analyze:
Flow behavior in internal and external systems (e.g., pipes, turbines).
Turbulence, pressure drops, and aerodynamics.
Multiphase flows, combustion, and chemical reactions.
Coupling of structural, thermal, electromagnetic, and fluid domains.
Example: Electro-thermal-mechanical analysis of actuators, MEMS devices.
Use parametric modeling and Design of Experiments (DOE) for optimizing component performance.
Example: Reduce weight while maintaining strength in an automotive suspension.
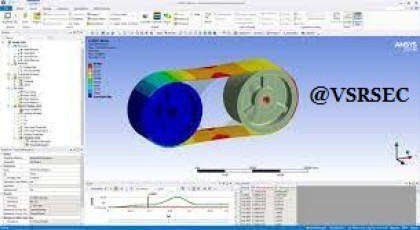
CO1: Understand the fundamentals of Finite Element Analysis (FEA) and the theoretical concepts behind simulation techniques using ANSYS.
CO2: Apply pre-processing techniques (geometry modeling, meshing, material selection, boundary condition application) in ANSYS for mechanical components.
CO3: Analyze structural systems under static, dynamic, and thermal loads using ANSYS Mechanical.
CO4: Simulate fluid flow and heat transfer problems using ANSYS Fluent/CFX and interpret the results.
CO5: Perform multiphysics simulations involving coupled thermal-structural or fluid-thermal-structural problems.
CO6: Evaluate the mechanical performance of engineering components through simulation and propose optimized design solutions.
CO7: Communicate simulation results effectively through post-processing tools (contour plots, animations, reports) and validate with analytical or experimental data.
0 Reviews
Review Course
For Review on Course. You need to Login first. Login Here