HTML Essentials: Build the Web from Scratch
Branch : CSE



This comprehensive online course is specifically designed to teach civil engineering students and professionals how to use AutoCAD, the industry-standard CAD software, for civil engineering drafting and design. The course covers essential 2D drafting and 3D modeling techniques applicable to civil projects such as site plans, road layouts, building foundations, topographic maps, and infrastructure designs.
Learners will gain hands-on experience in creating accurate technical drawings, interpreting civil engineering blueprints, and applying best practices to produce professional-grade designs. The curriculum emphasizes practical workflows tailored to civil engineering needs, including layers, dimensioning, annotations, and plot settings.
Whether you are a student aiming to enhance your academic projects or a professional seeking to upgrade your design skills, this course equips you with the tools to draft, visualize, and communicate civil engineering concepts effectively using AutoCAD.
Fundamentals of AutoCAD interface and commands
2D drafting and annotation specific to civil engineering
Creating site plans, road profiles, and contour maps
Introduction to 3D modeling for civil applications
Best practices for layering, dimensioning, and plotting
Hands-on projects simulating real-world civil engineering designs
Suitable for civil engineering students, junior engineers, and drafters
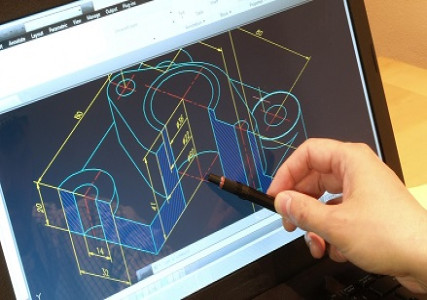
Understand and navigate the AutoCAD interface tailored for civil engineering drafting and design.
Create accurate 2D drawings including site plans, road layouts, and building foundations using civil engineering standards.
Apply layer management, dimensioning, and annotation techniques to produce clear and professional technical drawings.
Interpret and replicate civil engineering blueprints and survey data within AutoCAD.
Generate and modify contour maps and topographic drawings relevant to civil projects.
Develop basic 3D models of civil structures to aid in visualization and design validation.
Utilize plotting and printing tools to produce high-quality design documentation for field and office use.
Employ best practices for efficient drafting workflows specific to civil engineering projects.
Demonstrate readiness for civil engineering roles that require CAD drafting and design skills.
Integrate AutoCAD skills to enhance academic projects and professional civil engineering tasks.
0 Reviews
Review Course
For Review on Course. You need to Login first. Login Here